Shrimp is one of the favorite seafoods for most people. But if you are wondering whether you can have shrimp when breastfeeding, continue reading to find the answer.
Lactating mothers need to be extra careful about what they eat. Besides antibodies, the baby receives all its nutrients from you that get passed on through the breast milk. Therefore, at times, most mothers may need to sacrifice some of their favorite foods to protect their babies. For example, seafood or things that normally induce allergy in some people may also cause a reaction in your baby if taken in higher amounts. You may have to stick to consuming a specific amount of shrimps during lactation to avoid any potential adverse effects on the baby.
Read on to know more about shrimp consumption by nursing mothers, including its benefits and side effects.
What Is Shrimp?
Shrimp accounts for almost 25% of the seafood consumed in the US, (1). Shrimp is a rich source of antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids and is highly nutritious (2). Shrimps are crustaceansiXA group of invertebrate animals with three body segments, paired appendages, and a hard covering to protect the soft tissues., just like crabs and lobsters, which means they have an exoskeleton. Although the words “shrimp” and “prawns” are often used interchangeably, prawns inhabit freshwater habitats, and shrimp predominantly inhabit saltwater habitats. Shrimp is considered low in methyl mercuryiXA form of mercury that affects people through air and food and causes adverse health effects, including brain and nervous system damage. and hence can be consumed by a breastfeeding mother once in a while (3).
Is It Safe To Eat Shrimp While Breastfeeding?
Though shrimp is helpful for postpartum nutrition, but if you choose to breastfeed, you should limit the consumption to 12oz. per week. Breastfeeding mothers can eat two to three servings of fish a week, including shrimp (3). If you happen to consume more fish in a week, you can limit or reduce the consumption the next week to balance it out.
Consumimg shrimp while breastfeeding in a limited amount ensures optimal protein intake and iron intake (8). Also, make sure to check the signs of shellfish allergy in your baby and stop eating shrimp if your baby is irritable or shows any signs of a possible allergic reaction.
How To Purchase Shrimp While Breastfeeding?
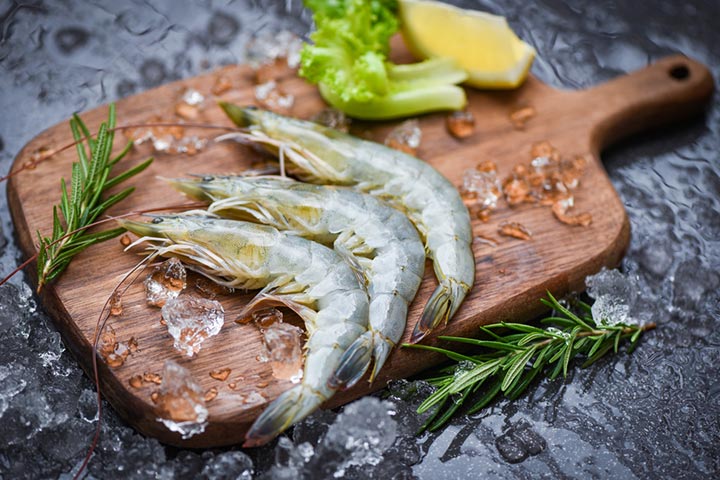
Like any other seafood, make sure to purchase shrimp from a well-known and hygienic store. The store should offer a fresh supply or speak to the fish dealer to have a fresh supply every time. While purchasing shrimp, you would also want to decide if you want fresh shrimp or the frozen kind. Frozen shrimp has a longer shelf life than fresh shrimp, and you can store it for a day or two. Color is a good indicator of the quality of the shrimp. Unless it is a spotted shrimp, you should not see any rings or spots on the skin—these may signify that the shrimp has gone bad.
How To Know The Shrimp Is Cooked Well?
You can determine if the shrimp is cooked correctly by checking its color. When shrimp is undercooked, it looks gray. However, when it’s cooked well, it turns white with hints of pink or red. Raw shrimp without shells are soft and appear longer because they’re straight. The ideal way to cook shrimp is to have them curl like the letter C. Undercooked shrimp are a bit straight or slightly curved and firm. While overcooked, they are tightly coiled like the letter O, tough and hard to chew. Perfectly cooked shrimp should be between the two.
Why Should You Limit Eating Shrimp While Breastfeeding?
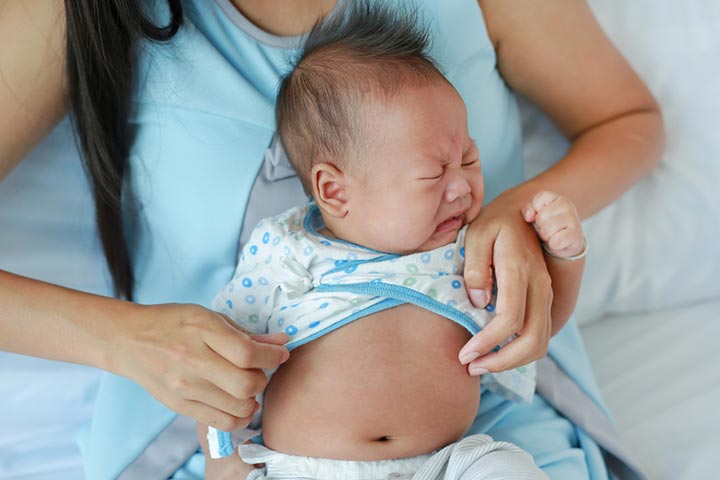
While it is a great source of omega-3 and fatty acids, shrimp contains mercury and other heavy metal contaminants, which can pass into your breastmilk. Excessive exposure to mercury through breast milk can harm babies’ nervous systems (4). Also, certain foods in mothers’ diets, like shrimp, can lead to gastrointestinal irritationiXA condition that inflames the gastrointestinal lining, causing indigestion, vomiting, and abdominal pain. and even cause allergic reactions in babies. Consult your pediatrician immediately if the baby becomes fussy or develops rashes, diarrhea, or congestion (5).
Side Effects Of Eating Shrimp While Breastfeeding
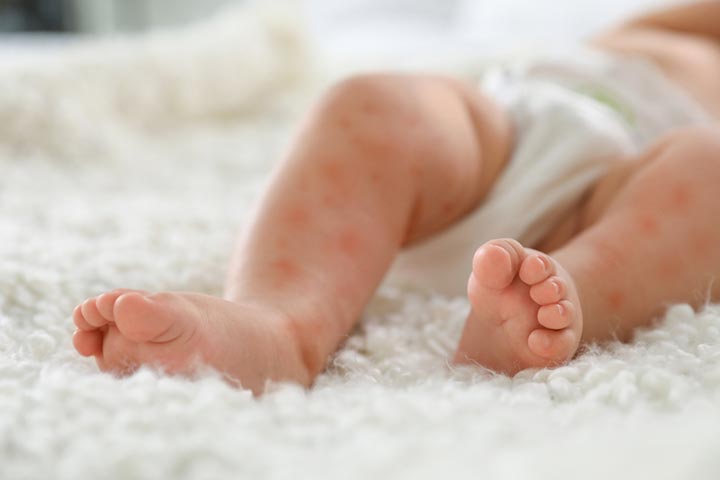
Breastfed babies sometimes develop allergies to foods through maternal diet. Common allergies in babies include soy, wheat, dairy, corn, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, and shellfish, including shrimp.
Signs of allergic reactions in babies include (5)
- Frequent vomiting and spitting up
- Belly pain, bloating, and excess gas
- Bloody and mucusiXA sticky material lining the lungs, throat, mouth, and nose and lubricates and shields the organs from viruses and allergens.-filled stools
- Hard stools (constipation) or diarrhea
- Skin rashes
- Wheezing and difficulty breathing
- Shock
If you see any of these signs in your baby, seek emergency medical advice and be sure to avoid the possible offending food in the future. If the problem continues, it’s essential to practice food safety practices and keep a list of everything you have throughout the day and share this “food diary” with your baby’s doctor. Your doctor might be able to help pinpoint the problematic food.
Shrimp is a nutritious shellfish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality lean protein, and several micronutrients. You can safely consume shrimp when breastfeeding as a part of a well-balanced diet. Be cautious of overeating shrimp as it contains mercury and other contaminants, which in high concentrations can adversely affect your and your nursing infant’s health. If you are eating shrimp for the first time, stay watchful for signs of allergy and intolerance. Discontinue eating shrimp and speak to your doctor if your nursing baby shows signs of discomfort after eating shrimp.
Key Pointers
- Shrimp is a highly nutritious food rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
- During pregnancy, it is crucial to consume shrimp in moderation, despite its low levels of mercury and other heavy metal contaminants.
- Babies may experience gastrointestinal irritation and allergic reactions from consuming shrimp.
- Some side effects of shrimp consumption include vomiting, bloating, excess gas, bloody or mucus-filled stool, skin rash, wheezing, and shock.
- If any of these symptoms are noticed, seek emergency medical advice.