Hypertonia in babies is a medical condition where high muscle tone or hypertonicity of muscle leads to muscle stiffness, leading to difficulty in limb movement. Usually, the central nervous system (CNS) regulates muscle tone by sending signals from the brain to the nerves in the muscles. If certain regions of the brain or spinal cord (the CNS) that control muscle tones are damaged, they cause hypertonia.
Some babies can have transient hypertonia that resolves in a short time, while a few may have persistent hypertonia that may stay for a lifetime. Hypertonia has less occurrence in babies than hypotonia (floppy baby syndrome) which affects a newborns motor skills.
Read on as we give you a brief overview of the causes, signs, risk factors, and treatment for hypertonia in babies.
Causes Of Hypertonia In Babies
Muscle tone is a muscle’s resistance to stretch. The muscle tone is regulated by the central nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and nerves) through nerve signals that contract and relax the muscle. In hypertonia, the nerve pathways that control the muscle are disrupted due to damage to the central nervous system (CNS).
The following conditions and factors may lead to CNS damage (1).
- Brain tumors
- Head injuries
- Stroke
- Neurotoxins
- Neurodevelopmental anomalies, such as cerebral palsyiXA set of disorders affecting a person’s ability to move, balance, and maintain proper postures
- Neurodegenerative diseasesiXA group of conditions caused by the disintegration of neurons, which impairs the proper functioning of the brain and the body
Babies who develop hypertonia after a fall or blow to the head should be taken to emergency care. Some of these conditions may also cause hypotonia (low infant muscle tone) or floppy baby syndrome. Consult a doctor to determine the precise underlying cause.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertonia
Hypertonia signs and symptoms may vary dependingon the severity of the damage and the part of the brain or spinal cord affected. Sometimes, a baby’s muscle tone may be high on both sides of the body, while a few may have it on one side.
Common signs and symptoms seen in hypertonia in babies include the following (2).
- Reduced range of motion
- Stiff or rigid muscles
- Body deformity
- Awkward muscle contractions
- Frozen or fixed joints
- Developmental delays such as inability to walk or stand as peers
- Involuntarily crossing of the legs
Brittany Frost, a mom and vlogger, shares the signs her daughter Lennon showed that eventually led to her hypertonia diagnosis. She says, “One of the first things we noticed was that her legs were stiff. She wasn’t bending them when we would hold her and feed her…Another thing is her jaw and her arms both shake, kind of like what you do when you’re cold and shiver…And then a new symptom she has is she’s not jumping or bouncing in any bouncer that we have…The physical therapist thinks that has something to do with her hypertonia and said something about her needing assistance with climbing stairs when she’s older (i).”
In another vlog, Frost shares these updates about Lennon, “ Lennon’s first MRI came back normal, but she was still very stiff, so we took her to another neurologist, and they had us go for a second MRI to check her spine to see if she had a tethered cord and that MRI also came back normal. The neurologists suggested using muscle relaxants and additional physical therapy. However, she did not need any additional muscle relaxants and walks and runs like a normal toddler now. She is very strong and not extremely tight anymore, and she moves around like any other toddler (ii).
According to the affected area of the brain, hypertonia can be spastic or rigid. Spasticity causes higher reflex responses and increased muscle spasms. Rigidity causes excessive stiffness of the muscles.
Diagnosis Of Hypertonia
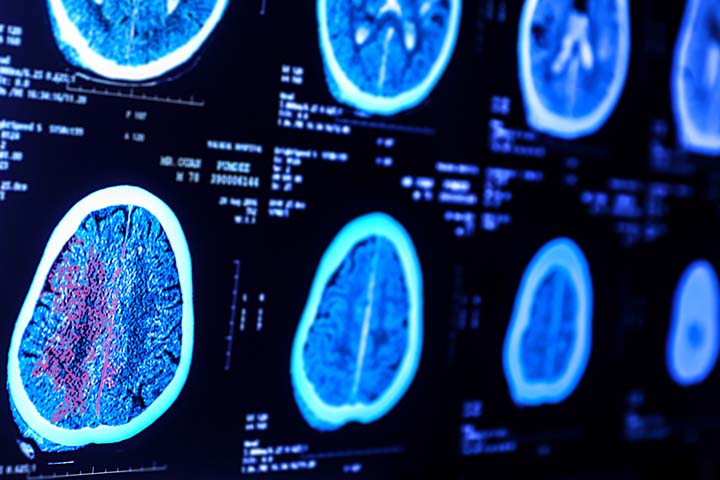
History of symptoms and physical examination can be enough to identify the presence of hypertonia in babies. Additional tests, such as blood test, CSF analysisiXA diagnostic method used to evaluate the cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of any diseases concerning the brain and spinal cord, and imaging tests (MRI scans), are ordered to look for brain anomalies (1).
Blood tests and CSF analysis help identify infections and determine neurotransmittersiXChemical messengers in the brain that send signals throughout the body to carry out its vital functions levels. Specific tumor markers and toxins can also be determined from blood tests. Neuroimaging helps visualize structural anomalies and intracranial hemorrhagesiXBleeding within the brain tissue often caused due to trauma or accidents, leading to emergency conditions such as stroke that often occur after head injuries.
Treatment For Hypertonia In Babies
The treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause. The following treatments could be prescribed for babies (1) (3).
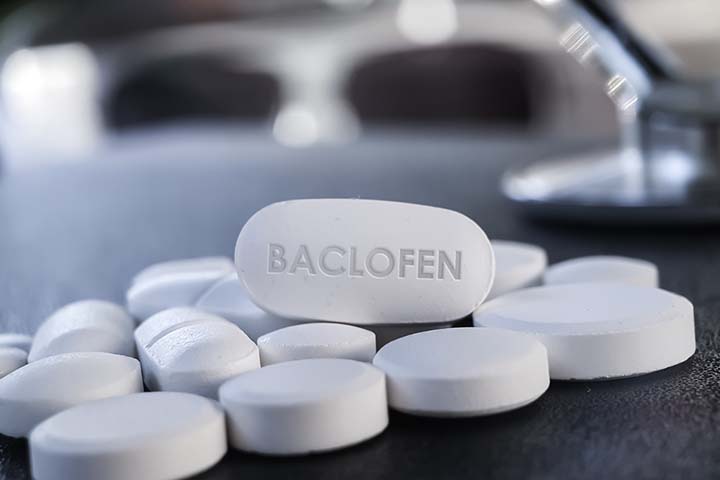
- Baclofen, a muscle relaxer and an antispasmodiciXMedications that reduce spasms, cramps, and intense pain drug, is prescribed as a first-line treatment for babies with brain anomalies.
- Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are also used in initial treatment for hypertonia due to brain problems.
- Vitamins are often prescribed for babies with seizures.
- Levodopa, a type of amino acid, is given to babies with CNS-related causes but with no abnormalities seen in neuroimaging tests.
- Carbamazepine and phenytoin are prescribed for peripheral nervous system-related causes of hypertonia.
- Botox (botulinum toxin) injections could be given to relax hypertonic muscles.
- Physiotherapy could be conducted, often in conjunction with other treatments, to improve muscle tone.
If hypertonia is a result of another condition, it could also be treated simultaneously.
Prognosis Of Hypertonia In Babies
The outcome may vary based on the severity of hypertonia and the underlying cause. Hypertonia with cerebral palsy may often stay without change over a lifetime. In some cases, the hypertonia may worsen as the underlying condition worsens over time (4).
Mild hypertonia may cause no effect as the baby grows older. In contrast, moderate hypertonia may increase the risk of abnormal joint contractions, which increase the risk of falls. Severe hypertonia could increase the risk of several complications, such as fractures, bedsores, infections, and severe immobility.
Hypertonia in babies is characterized by excessive muscle stiffness leading to problems with movement. It can be caused by problems with the central nervous system due to tumors, injuries, blows, trauma, and some diseases. Hypertonia can be unilateral or bilateral, and the symptoms and severity may depend on the area of the brain involved. The doctor may diagnose the condition with a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging tests. Physical and occupational therapy over a prolonged period can improve the condition and promote motor development and help them perform activities like their peers.
Key Pointers
- Excessive muscle tone causing stiffness of the limbs is termed hypertonia.
- Some babies can have transitory or short-lived hypertonia, whereas others may have permanent hypertonia.
- Disruption of the nerve pathways that control the muscles due to damage to the central nervous system (CNS) is its main cause.
- Prompt diagnosis is essential to determine the precise cause and initiate the treatment to manage the condition.