Congenital herpes or birth-acquired herpes infection is a viral infection acquired by babies during delivery or in the womb. Babies born with herpes may show symptoms of the infection at birth or may develop them shortly after birth. Pregnant women with genital herpes may transmit the virus to their babies during vaginal delivery.
Herpes infection can cause lifelong complications that can often be life-threatening if left untreated. Hence, this post tells you more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, complications, treatment, prevention, and outcomes of birth-acquired herpes in babies.
Causes Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
Herpes infection is a contagious viral disease caused by the following strains of herpes virus(1).
- Herpes simplex type 1 (HSV 1) causes cold sores around or inside the mouth.
- Herpes simplex type 2 (HSV 2) causes genital herpes infection.
Infants can contract herpes from inactive (no symptoms) or active (having blisters in the birth canal) maternal herpes infection. Once infected, the herpes virus stays dormant within the body and may cause recurrent infection during favorable circumstances, such as low immunity. Therefore, it’s crucial to be aware of herpes in newborns to ensure your little one’s health and safety.
Note: Herpes contracted from cold sores after birth is considered a neonatal herpes infection and not a congenital herpes infection.
Signs And Symptoms Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
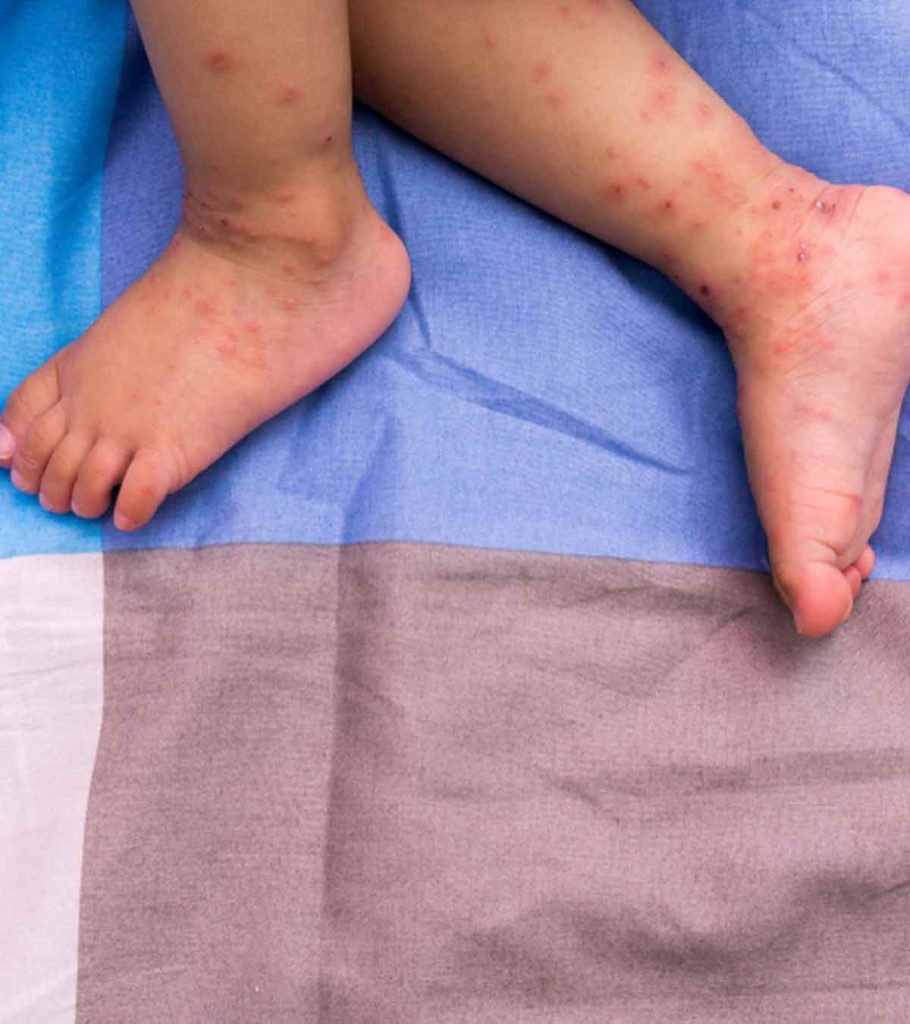
Some babies may only have skin lesions during herpes infection. A few babies could develop systemic herpes infection, which affects various organs of the body. When the baby has herpetic lesions on the skin and systemic herpes infection, it is called disseminated herpes.
The following signs and symptoms are seen in congenital herpes infection (2).
- Blisters (fluid-filled bumps) or vesicles on the skin
- Lethargy
- Breathing issues
- Bleeding-related problems
- Trouble feeding
- Jaundice
Fluid-filled blisters are commonly seen around the eyes or on the torso in congenital herpes infection. The blisters can burst and crust over time.
Diagnosis Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
The appearance of skin lesions helps diagnose herpes simplex infection in babies. The culture of a sample from the lesion helps confirm the diagnosis. Doctors may also check for enlarged lymph nodes in the groin and neck area.
Blood, cerebrospinal fluidiXA fluid present in and around the brain and spinal cord., and urine analyses are often ordered if the baby has a herpes infection. An eye examination is recommended since eye herpes is common in birth-acquired herpes infection. MRI scan of the head is often ordered to check for brain swelling or brain damage, especially if the CSF analysisiXA diagnostic method used to assess the cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of any diseases concerning the brain and spinal cord. is positive for the herpes virus (3).
Treatment For Birth-Acquired Herpes
Herpes symptoms in newborns are carefully considered to determine the appropriate course of action. Intravenous antiviral medications, such as acyclovir (Zovirax), are recommended for infants with herpes for a few weeks (1).
Topical ophthalmiciXConditions relating to the eye. drugs are given along with systemic antiviral therapy for babies with herpes eye infections. An ophthalmologist’s review will assist with a proper assessment.
Possible Complications Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
The following complications may occur in disseminated herpes virus infection.
- Seizures
- Eye inflammation
- Blindness and vision issues
- Respiratory problems
- Shock
- Hypothermia
- Coma
Seizures, shock, and hypothermia can be due to brain herpes infection (Herpes encephalitisiXA severe inflammatory brain condition resulting from an infection or autoimmune response. ), and this may often result in brain damage.
Prevention Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
The following precautions may reduce the risk of congenital herpes.
- Taking antiviral medications during the last weeks of pregnancy to reduce the risk of transmission
- Choosing cesarean delivery if the mother has genital herpes–this measure can effectively reduce the risk of herpes transmission during birth.
- Practicing safe sex during pregnancy
Prognosis Of Birth-Acquired Herpes
Skin lesions may reoccur even after the treatment. Babies with systemic herpes or encephalitis may have a poorer prognosis than babies with skin lesions. Although antiviral therapy may help subside active infection, herpes may come back if there are favorable conditions since the virus remains dormant in the body.
Disseminated congenital herpes can result in neurological issues or coma, which can be life-threatening. Babies with systemic herpes infection may develop other potential health problems based on the organ affected.
Herpes virus cannot be eliminated from the body, but babies born with herpes may be treated with antiviral medications and supportive therapy. Babies may contract the virus from active as well as dormant maternal infection. Untreated herpes infection may have life-threatening consequences such as shock or coma. Check with your doctor if the baby develops skin lesions, breathing trouble, or jaundice. Transmission of active herpes from mother to child may be prevented by avoiding vaginal delivery and antiviral treatment of the mother during late pregnancy.
Key Pointers
- Congenital herpes is a condition where babies develop a viral herpes infection in the mother’s womb or during the birth process.
- This infection might give rise to complications such as respiratory problems and seizures in newborns.
- Talk to a pediatrician if your baby develops blisters or shows signs of fatigue, trouble breathing, and feeding.
- Though we cannot eliminate the infection, it is manageable by antiviral medications.
Learn how to treat cold sores on babies safely and effectively. Check out this informative video and get some tips on how to soothe and protect your little one’s skin.